NCTF 2025
NCTF 2025 writeup
For official writeup, here.
gogo
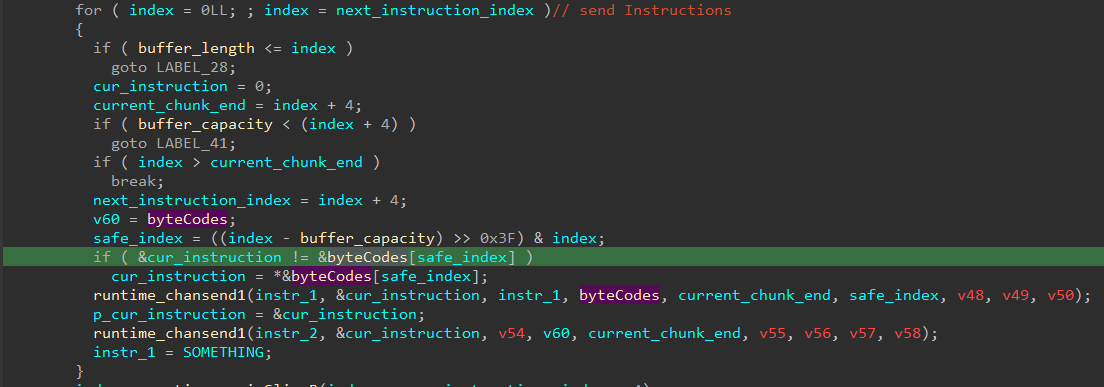
Input 40 bytes and create two coroutine (coroutVM), processing 20Bytes respectively
What we need: hash table & bytecodes
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
struct main_coroutVM // sizeof=0x158
{
_16_uint32 reg;
_256_uint8 mem;
_chan_left_chan__4_uint8 instr;
chan_bool checkres;
map_uint8_main_handler instrSet;
};
Method 1 - Static Analysis
Find bytecode and hash table, then write a script to disassemble
Bytecode
Extract hash table
Each pair is set by:
runtime_mapassign(..., key_x[i], ...) + if(isGC)... + *variable = &handler[j];
Extract the hash table
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
{
0x11: "main_LDR",
0x12: "main_LDRI",
0x15: "main_STR",
0x16: "main_STRI",
0x2A: "main_MOV",
0x41: "main_ADD",
0x42: "main_SUB",
0x47: "main_MUL",
0x71: "main_LSL",
0x73: "main_LSR",
0x7A: "main_XOR",
0x7B: "main_AND",
0xFE: "main_RET",
0xFF: "main_HLT"
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
{
0x13: main_LDR,
0x14: main_LDRI,
0x17: main_STR,
0x18: main_STRI,
0x2B: main_MOV,
0x91: main_ADD,
0x92: main_SUB,
0x97: main_MUL,
0xC1: main_LSL,
0xC3: main_LSR,
0xCA: main_XOR,
0xCB: main_AND,
0xFE: main_RET,
0xFF: main_HLT
}
Disassembly
Based on the handler function for each opcode, we know:
- Both VM emulate ARM32 instruction set
- Both use the same set of handler functions
- The bytecodes of two VM are mixed together, only the opcodes that match the respective VM will be executed
Info on hand:
- Hash tables for different VM
- Instruction structure:
Opcode+Oprand * 3, total 4Bytes - Dumped bytecode (
DumpedByteCodes.bin)
| Instruction | Operands | Operand 1 (Byte a10) | Operand 2 (Byte a11) | Operand 3 (Byte a12) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADD/SUB/MUL/XOR/AND | 3 | Rd (reg index) | Rn (reg index) | Rm (reg index) |
| LSL/LSR | 3 | Rd (reg index) | Rn (value reg) | Rm (shift amt reg) |
| MOV | 2 | Rd (reg index) | Immediate val (WORD little endian) | |
| STRI/LDRI | 2 | Rd (reg index) | Must be 0x00 | Immediate val (addr) |
| LDR/STR | 2 | Rd (reg index) | Rn (addr) | Must be 0x00 |
Based on the hash table & instruction set, write a script to read file DumpedByteCodes.bin and disassemble bytecode for two VM respectively, outputting to two .asm files.
movzx edx, [rsp+10h+oprand_3]inSTRI. Zero-extend this byte into the 32-bit edx register. The upper 24 bits of edx are set to 0.Note that this implicitly zeros the upper 32 bits of rdx as well in x86-64). Let’s call the byte value
val3.rdxbecomes0x00000000000000XXwhereXXisval3.
Disassembly script:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
import struct
import os
# --- Configuration ---
# Define Opcode Mappings (Using simplified mnemonics for clarity)
VM1_OPS = {
0x11: "LDR", 0x12: "LDRI", 0x15: "STR", 0x16: "STRI",
0x2A: "MOV", 0x41: "ADD", 0x42: "SUB", 0x47: "MUL",
0x71: "LSL", 0x73: "LSR", 0x7A: "XOR", 0x7B: "AND",
0xFE: "RET", 0xFF: "HLT"
}
VM2_OPS = {
0x13: "LDR", 0x14: "LDRI", 0x17: "STR", 0x18: "STRI",
0x2B: "MOV", 0x91: "ADD", 0x92: "SUB", 0x97: "MUL",
0xC1: "LSL", 0xC3: "LSR", 0xCA: "XOR", 0xCB: "AND",
0xFE: "RET", 0xFF: "HLT"
}
INPUT_FILE = "DumpedByteCodes.bin"
OUTPUT_VM1_FILE = "vm1_disassembly.asm"
OUTPUT_VM2_FILE = "vm2_disassembly.asm"
INSTRUCTION_SIZE = 4 # bytes
# --- Operand Parsing Logic ---
def parse_operands(mnemonic, b1, b2, b3):
"""
Parses operand bytes based on the instruction mnemonic.
Returns a formatted string representation of the operands.
"""
try:
if mnemonic in ["ADD", "SUB", "MUL", "XOR", "AND", "LSL", "LSR"]:
return f"R{b1}, R{b2}, R{b3}"
elif mnemonic == "MOV":
imm = (b3 << 8) | b2
return f"R{b1}, #{imm:#06x}"
elif mnemonic in ["LDRI", "STRI"]:
if b2 != 0x00:
print(f"Warning: Expected 0x00 for operand 2 in {mnemonic} (Opcode byte 2), got {b2:#04x}")
return f"R{b1}, [#{b3:#04x}]"
elif mnemonic in ["LDR", "STR"]:
if b3 != 0x00:
print(f"Warning: Expected 0x00 for operand 3 in {mnemonic} (Opcode byte 3), got {b3:#04x}")
return f"R{b1}, [R{b2}]"
elif mnemonic in ["RET", "HLT"]:
return ""
else:
print(f"Warning: Unknown mnemonic '{mnemonic}' during operand parsing.")
return f"?? DB 0x{b1:02X}, 0x{b2:02X}, 0x{b3:02X}"
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error parsing operands for {mnemonic} with bytes {b1}, {b2}, {b3}: {e}")
return f"!! PARSE ERROR !!"
# --- Main Disassembly Function ---
def disassemble():
"""
Reads the bytecode file and performs disassembly for both VMs,
including the raw bytes in the output.
"""
if not os.path.exists(INPUT_FILE):
print(f"Error: Input file '{INPUT_FILE}' not found.")
return
processed_instructions = 0
unknown_opcodes = 0
try:
with open(INPUT_FILE, 'rb') as f_in, \\
open(OUTPUT_VM1_FILE, 'w') as f_out1, \\
open(OUTPUT_VM2_FILE, 'w') as f_out2:
print(f"Starting disassembly of '{INPUT_FILE}'...")
# Add header explaining the format
header_format = "; Format: Offset Bytes Instruction\\n"
f_out1.write(f"; --- VM1 Disassembly from {INPUT_FILE} ---\\n")
f_out1.write(header_format)
f_out2.write(f"; --- VM2 Disassembly from {INPUT_FILE} ---\\n")
f_out2.write(header_format)
offset = 0
while True:
chunk = f_in.read(INSTRUCTION_SIZE)
if not chunk:
break
if len(chunk) < INSTRUCTION_SIZE:
print(f"Warning: Trailing {len(chunk)} byte(s) at offset 0x{offset:08X}, ignored.")
break
try:
b0, b1, b2, b3 = struct.unpack('<BBBB', chunk)
except struct.error:
print(f"Error: Could not unpack 4 bytes at offset 0x{offset:08X}.")
break
offset_str = f"0x{offset:08X}:"
# Format the raw bytes as hex strings, separated by spaces
byte_str = ' '.join(f"{byte:02X}" for byte in chunk)
# Pad the byte string for alignment (4 bytes * 2 hex chars + 3 spaces = 11 chars)
# Use padding of 12 for a bit extra space.
padded_byte_str = f"{byte_str:<12}"
vm1_mnemonic = VM1_OPS.get(b0)
vm2_mnemonic = VM2_OPS.get(b0)
instruction_part = "" # The mnemonic and operands part
target_files = []
if vm1_mnemonic and vm2_mnemonic: # Shared opcode
mnemonic = vm1_mnemonic
operands_str = parse_operands(mnemonic, b1, b2, b3)
instruction_part = f"{mnemonic:<5} {operands_str}".strip()
target_files.extend([f_out1, f_out2])
elif vm1_mnemonic: # VM1 specific
mnemonic = vm1_mnemonic
operands_str = parse_operands(mnemonic, b1, b2, b3)
instruction_part = f"{mnemonic:<5} {operands_str}".strip()
target_files.append(f_out1)
elif vm2_mnemonic: # VM2 specific
mnemonic = vm2_mnemonic
operands_str = parse_operands(mnemonic, b1, b2, b3)
instruction_part = f"{mnemonic:<5} {operands_str}".strip()
target_files.append(f_out2)
else: # Opcode not found in either map
print(f"Warning: Unknown opcode 0x{b0:02X} at offset {offset_str}")
unknown_opcodes += 1
# Represent unknown opcodes clearly in the output
instruction_part = f"; --- UNKNOWN OPCODE {b0:#04x} ---"
# Write unknown lines to both files for completeness
target_files.extend([f_out1, f_out2])
# Construct the final disassembled line including bytes
disassembled_line = f"{offset_str} {padded_byte_str} {instruction_part}"
# Write the line to the determined target file(s)
for f_out in target_files:
f_out.write(disassembled_line + "\\n")
processed_instructions += 1
offset += INSTRUCTION_SIZE
print("-" * 30)
print(f"Disassembly complete.")
print(f"Processed {processed_instructions} instructions ({processed_instructions * INSTRUCTION_SIZE} bytes).")
if unknown_opcodes > 0:
print(f"Encountered {unknown_opcodes} unknown opcodes.")
print(f"VM1 output saved to '{OUTPUT_VM1_FILE}'")
print(f"VM2 output saved to '{OUTPUT_VM2_FILE}'")
except IOError as e:
print(f"Error handling files: {e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An unexpected error occurred: {e}")
# --- Run the Disassembler ---
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Run the main function
disassemble()
Key takeaways of the two disasm code:
; --- VM1 Disassembly from DumpedByteCodes.bin ---
; Offset Bytes Instruction
...
0x00000020: 16 01 00 1C STRI R1, [#0x1c] ; 0x9e3779b9
0x00000044: 12 02 00 04 LDRI R2, [#0x04] ; y
0x0000004C: 12 03 00 10 LDRI R3, [#0x10] ; z
0x00000064: 71 04 02 00 LSL R4, R2, R0 ; y << 2
0x0000006C: 73 05 03 0F LSR R5, R3, R15 ; z >> 5
0x00000070: 7A 06 04 05 XOR R6, R4, R5 ; (z >> 5) ^ (y << 2)
0x00000088: 73 04 02 00 LSR R4, R2, R0 ; y >> 3
0x00000098: 71 05 03 0F LSL R5, R3, R15 ; z << 4
0x0000009C: 7A 07 04 05 XOR R7, R4, R5 ; (y >> 3) ^ (z << 4)
0x000000A0: 41 08 06 07 ADD R8, R6, R7 ; ((z >> 5) ^ (y << 2)) + ((y >> 3) ^ (z << 4))
0x000000CC: 16 05 00 28 STRI R5, [#0x28] ; 0xa78c0b4f
0x000000DC: 73 09 01 0F LSR R9, R1, R15 ; sum >> 2
0x000000E8: 7B 0D 09 00 AND R13, R9, R0 ; (sum >> 2) & 3
0x000000EC: 7A 04 0D 0E XOR R4, R13, R14; p ^ ( (sum >> 2) & 3 )
0x000000F4: 7B 04 04 00 AND R4, R4, R0 ; p ^ ( (sum >> 2) & 3 ) & 3
0x00000104: 47 04 04 0C MUL R4, R4, R12 ; idx * 4
0x00000110: 41 0A 04 0F ADD R10, R4, R15; (idx * 4) + 0x20
0x0000011C: 11 04 0A 00 LDR R4, [R10] ; key[p ^ ( (sum >> 2) & 3 ) & 3]
0x00000120: 7A 06 01 02 XOR R6, R1, R2 ; sum ^ y
0x00000128: 7A 07 03 04 XOR R7, R3, R4 ; z ^ key[p]
0x0000012C: 41 09 06 07 ADD R9, R6, R7 ; (sum ^ y) + (z ^ key[p ^ e & 3])
0x0000013C: 7A 0A 08 09 XOR R10, R8, R9 ; ((z >> 5) ^ (y << 2)) + ((y >> 3) ^ (z << 4)) ^ ((sum ^ y) + (key[(p & 3) ^ e] ^ z))
0x00000168: 16 05 00 20 STRI R5, [#0x20] ; 0x6e637466
0x000001D8: 16 05 00 24 STRI R5, [#0x24] ; 0x062ef0ed
0x000001DC: 12 02 00 08 LDRI R2, [#0x08] ; y
0x000001E0: 12 03 00 00 LDRI R3, [#0x00] ; z
0x000001F8: 71 04 02 00 LSL R4, R2, R0 ; << 2
0x00000208: 73 05 03 0F LSR R5, R3, R15 ; >> 5
0x00000268: 16 05 00 2C STRI R5, [#0x2c] ; 0x32303234
; --- VM2 Disassembly from DumpedByteCodes.bin ---
; Offset Bytes Instruction
0x0000002C: 91 01 01 03 ADD R1, R1, R3 ;0x9e3779b9
0x00000048: 2B 0E 00 00 MOV R14, #0x0000; p = 0
0x00000054: 14 02 00 04 LDRI R2, [#0x04] ; y
0x00000058: 14 03 00 10 LDRI R3, [#0x10] ; z
0x00000074: C3 04 02 00 LSR R4, R2, R0 ; y >> 2
0x00000078: C1 05 03 0F LSL R5, R3, R15 ; z << 5
0x0000007C: CA 06 04 05 XOR R6, R4, R5 ; (z << 5) ^ (y >> 2)
0x00000094: C1 04 02 00 LSL R4, R2, R0 ; y << 3
0x000000A4: C3 05 03 0F LSR R5, R3, R15 ; z >> 4
0x000000B0: CA 07 04 05 XOR R7, R4, R5 ; (y << 3)(z >> 4)
0x000000B4: 91 08 06 07 ADD R8, R6, R7 ; (z << 5) ^ (y >> 2) + (y << 3) ^ (z >> 4)
0x000000E4: 18 05 00 28 STRI R5, [#0x28] ; 0x9f1cf72e
0x000000F8: C3 09 01 0F LSR R9, R1, R15 ; sum >> 2
0x000000FC: CB 0D 09 00 AND R13, R9, R0 ; (sum >> 2) & 3
0x0000010C: CA 04 0D 0E XOR R4, R13, R14; (sum >> 2) & 3 ^ p
0x00000114: CB 04 04 00 AND R4, R4, R0 ; idx = (p & 3) ^ ( (sum >> 2) & 3 )
0x00000124: 97 04 04 0C MUL R4, R4, R12 ; idx * 4
0x00000134: 91 0A 04 0F ADD R10, R4, R15; 0x20 + idx * 4
0x00000138: 13 04 0A 00 LDR R4, [R10] ; mem[0x20 + idx * 4]
0x00000140: CA 06 01 02 XOR R6, R1, R2 ; sum ^ y
0x00000150: CA 07 03 04 XOR R7, R3, R4 ; mem[0x20 + idx * 4] ^ z
0x00000154: 91 09 06 07 ADD R9, R6, R7 ; (sum ^ y) + (mem[0x20 + idx * 4] ^ z)
0x00000158: CA 0A 08 09 XOR R10, R8, R9 ; (z << 5) ^ (y >> 2) + (y << 3) ^ (z >> 4) + (sum ^ y) + (mem[0x20 + idx * 4] ^ z)
0x00000184: 18 05 00 20 STRI R5, [#0x20] ; 0x32303234
0x000001D0: 18 05 00 24 STRI R5, [#0x24] ; 0xd6eb12c3
0x00000270: 18 05 00 2C STRI R5, [#0x2c] ; 0x4e435446
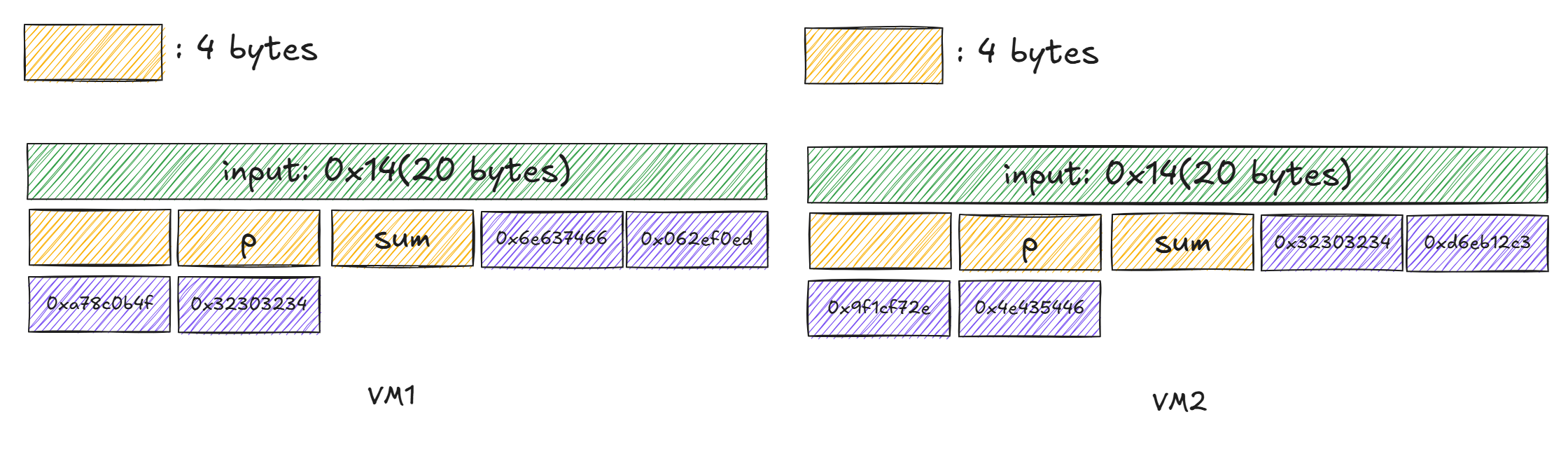
Memory layout of the two VM:
Decrypt script:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define DELTA 0x9e3779b9
void XXTEA_decrypt1(uint32_t *v, int n, const uint32_t key[4]) {
if (n < 2) return;
uint32_t y, z, sum, e;
int p, q = 6 + 52 / n;
sum = q * DELTA;
y = v[0];
do {
e = (sum >> 2) & 3;
for (p = n - 1; p > 0; p--) {
z = v[p - 1];
v[p] -= ((z >> 5) ^ (y << 2)) + ((y >> 3) ^ (z << 4)) ^ ((sum ^ y) + (key[(p & 3) ^ e] ^ z));
y = v[p];
}
z = v[n - 1];
v[0] -= ((z >> 5) ^ (y << 2)) + ((y >> 3) ^ (z << 4)) ^ ((sum ^ y) + (key[(p & 3) ^ e] ^ z));
y = v[0];
sum -= DELTA;
} while (--q > 0);
}
void XXTEA_decrypt2(uint32_t *v, int n, const uint32_t key[4]) {
if (n < 2) return;
uint32_t y, z, sum, e;
int p, q = 6 + 52 / n;
sum = q * DELTA;
y = v[0];
do {
e = (sum >> 2) & 3;
for (p = n - 1; p > 0; p--) {
z = v[p - 1];
v[p] -= ((z << 5) ^ (y >> 2)) + ((y << 3) ^ (z >> 4)) ^ ((sum ^ y) + (key[(p & 3) ^ e] ^ z));
y = v[p];
}
z = v[n - 1];
v[0] -= ((z << 5) ^ (y >> 2)) + ((y << 3) ^ (z >> 4)) ^ ((sum ^ y) + (key[(p & 3) ^ e] ^ z));
y = v[0];
sum -= DELTA;
} while (--q > 0);
}
int main()
{
uint32_t key1[] = {0x6e637466, 0x062ef0ed, 0xa78c0b4f, 0x32303234};
unsigned char cipher1[] =
{
0x5D, 0x45, 0xD5, 0xB9, 0x8C, 0x95, 0x9C, 0x38, 0x3B, 0xB1,
0x3E, 0x1E, 0x5F, 0xC8, 0xE8, 0xBB, 0x64, 0x38, 0x48, 0x69
};
size_t cipher_len_bytes = sizeof(cipher1);
int n = cipher_len_bytes / sizeof(uint32_t);
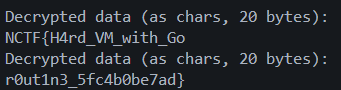
XXTEA_decrypt1((uint32_t *)cipher1, n, (const uint32_t *)key1);
// output
printf("\\nDecrypted data (as chars, %zu bytes):\\n", cipher_len_bytes);
for (size_t i = 0; i < cipher_len_bytes; i++)
{
if (cipher1[i] >= 32 && cipher1[i] <= 126) {
printf("%c", cipher1[i]);
} else {
printf(".");
}
}
uint32_t key2[] = {0x32303234, 0xd6eb12c3, 0x9f1cf72e, 0x4e435446};
unsigned char cipher2[] =
{
0xDE, 0x81, 0xD8, 0xAD, 0xC2, 0xC4, 0xA6, 0x32, 0x1C, 0xAB,
0x61, 0x3E, 0xCB, 0xFF, 0xEF, 0xF1, 0x27, 0x30, 0x7A, 0x16
};
XXTEA_decrypt2((uint32_t *)cipher2, n, (const uint32_t *)key2);
// output
printf("\\nDecrypted data (as chars, %zu bytes):\\n", cipher_len_bytes);
for (size_t i = 0; i < cipher_len_bytes; i++)
{
if (cipher2[i] >= 32 && cipher2[i] <= 126) {
printf("%c", cipher2[i]);
} else {
printf(".");
}
}
return 0;
}
/*
std TEA
void XXTEA_encrypt(uint32_t *v, int n, const uint32_t key[4]) {
if (n < 2) return; // At least two elements
uint32_t y, z, sum = 0, e;
int p, q = 6 + 52 / n; // Rounds
z = v[n - 1]; // | z(>>5 <<4) | v[p] | y(>>3 <<2) |
do {
sum += DELTA;
e = (sum >> 2) & 3;
for (p = 0; p < n - 1; p++) {
y = v[p + 1];
v[p] += ((z >> 5) ^ (y << 2)) + ((y >> 3) ^ (z << 4)) ^ ((sum ^ y) + (key[(p & 3) ^ e] ^ z));
z = v[p];
}
y = v[0];
v[n - 1] += ((z >> 5) ^ (y << 2)) + ((y >> 3) ^ (z << 4)) ^ ((sum ^ y) + (key[(p & 3) ^ e] ^ z));
z = v[n - 1];
} while (--q > 0);
}
*/
Method 2 - IDAPython
Instruction set:
Each handler function’s oprands are stack passing:
| Oprand 1 | `^0.1` |
| Oprand 2 | `^1.1` |
| Oprand 3 | `^2.1` |
Write IDA python script to set “trace” breakpoint and hook registers:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
import idaapi
import idc
def set_python_bpt(ea, cond):
''' 设置跟踪断点:触发时执行 Python 代码并继续执行 '''
# 检查地址是否有效
if not idaapi.is_mapped(ea):
print(f"[错误] 地址 {ea:x} 不在当前加载的模块中")
return
# 添加断点(类型:软件断点,默认行为)
if not idaapi.add_bpt(ea, 0, idaapi.BPT_SOFT):
print(f"[错误] 无法在地址 {ea:x} 添加断点")
return
# 配置断点属性
bpt = idaapi.bpt_t()
if not idaapi.get_bpt(ea, bpt):
print(f"[错误] 无法获取地址 {ea:x} 的断点信息")
return
bpt.elang = 'Python' # 使用 Python 条件
bpt.condition = cond # 条件表达式
bpt.flags |= idaapi.BPT_ENABLED # 启用断点
bpt.flags &= ~idaapi.BPT_BRK # 触发后不暂停程序(关键修改)
if not idaapi.update_bpt(bpt):
print(f"[错误] 无法更新地址 {ea:x} 的断点")
return
print(f"[成功] 在地址 {ea:x} 设置跟踪断点")
# ------------------------- 钩子函数定义 -------------------------
def hook_shr():
rbx = idc.get_reg_value("rbx")
cl = idc.get_reg_value("cl")
val1 = rbx
val2 = cl
print(f"{val1:x} >> {val2:x} = {(val1 >> val2) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF:x}")
def hook_shl():
rbx = idc.get_reg_value("rbx")
cl = idc.get_reg_value("cl")
val1 = rbx
val2 = cl
print(f"{val1:x} << {val2:x} = {(val1 << val2) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF:x}")
def hook_add():
rdx = idc.get_reg_value("rdx")
rax = idc.get_reg_value("rax")
rbx = idc.get_reg_value("rbx")
val1 = rdx
val2 = idc.get_qword(rax + rbx*4)
print(f"{val1:x} + {val2:x} = {(val1 + val2) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF:x}")
def hook_xor():
rdx = idc.get_reg_value("rdx")
rax = idc.get_reg_value("rax")
rbx = idc.get_reg_value("rbx")
val1 = rdx
val2 = idc.get_qword(rax + rbx*4)
print(f"{val1:x} ^ {val2:x} = {(val1 ^ val2) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF:x}")
def hook_sub():
rdx = idc.get_reg_value("rdx")
rax = idc.get_reg_value("rax")
rbx = idc.get_reg_value("rbx")
val1 = rdx
val2 = idc.get_qword(rax + rbx*4)
print(f"{val1:x} - {val2:x} = {(val1 - val2) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF:x}")
def hook_mul():
rdx = idc.get_reg_value("rdx")
rbx = idc.get_reg_value("rbx")
val1 = rdx
val2 = rbx
print(f"{val1:x} * {val2:x} = {(val1 * val2) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF:x}")
def hook_and():
rdx = idc.get_reg_value("rdx")
rax = idc.get_reg_value("rax")
rbx = idc.get_reg_value("rbx")
val1 = rdx
val2 = idc.get_qword(rax + rbx*4)
print(f"{val1:x} & {val2:x} = {(val1 & val2) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF:x}")
# ------------------------- 设置断点 -------------------------
# 设置跟踪断点列表(地址需根据实际情况调整)
trace_bpts = [
(0x0000000000848860, 'hook_shr()'),
(0x0000000000848820, 'hook_shl()'),
(0x000000000084871D, 'hook_add()'),
(0x00000000008487DD, 'hook_xor()'),
(0x000000000084875D, 'hook_sub()'),
(0x00000000008487A0, 'hook_mul()'),
(0x000000000084889D, 'hook_and()')
]
for ea, cond in trace_bpts:
set_python_bpt(ea, cond)
ezDOS
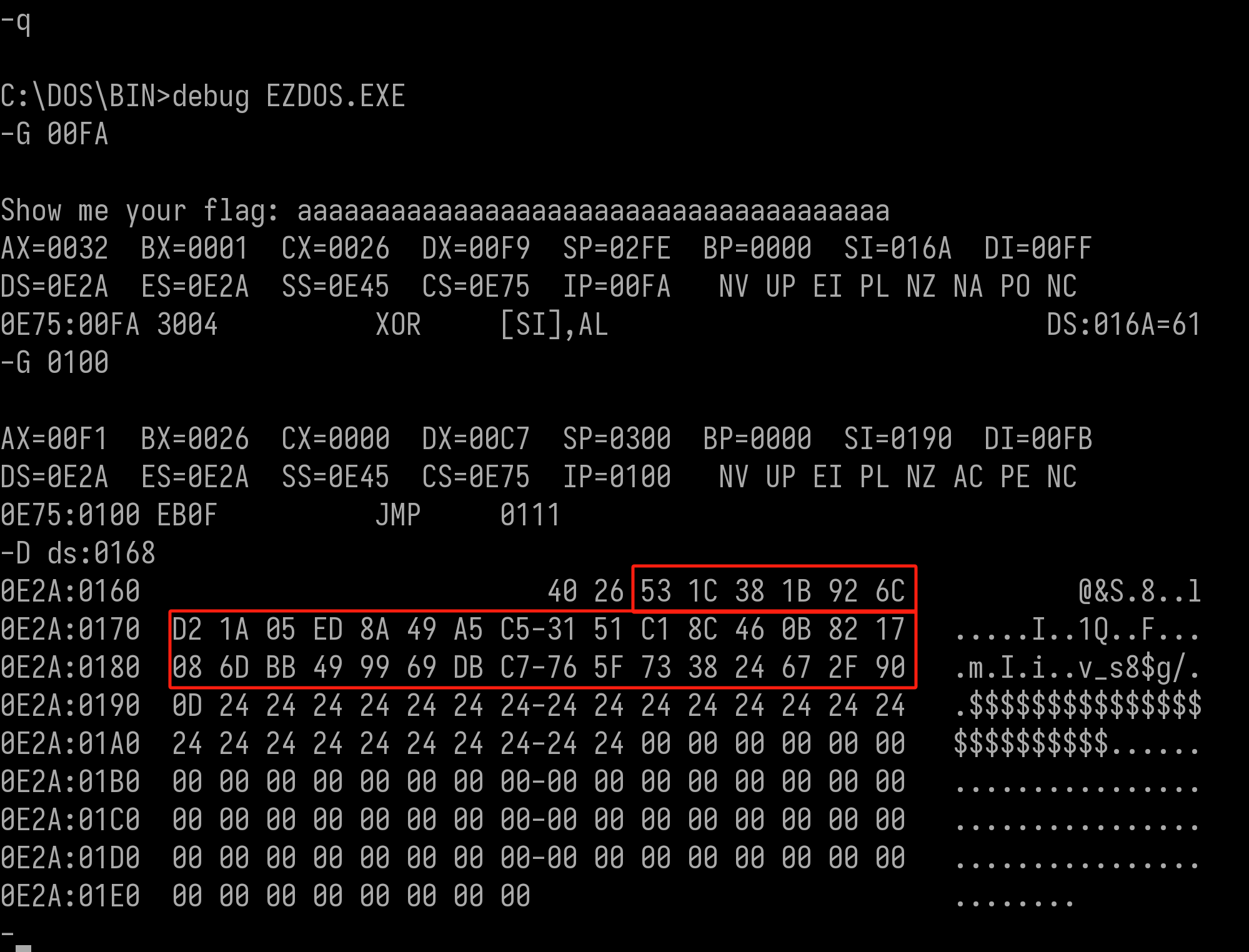
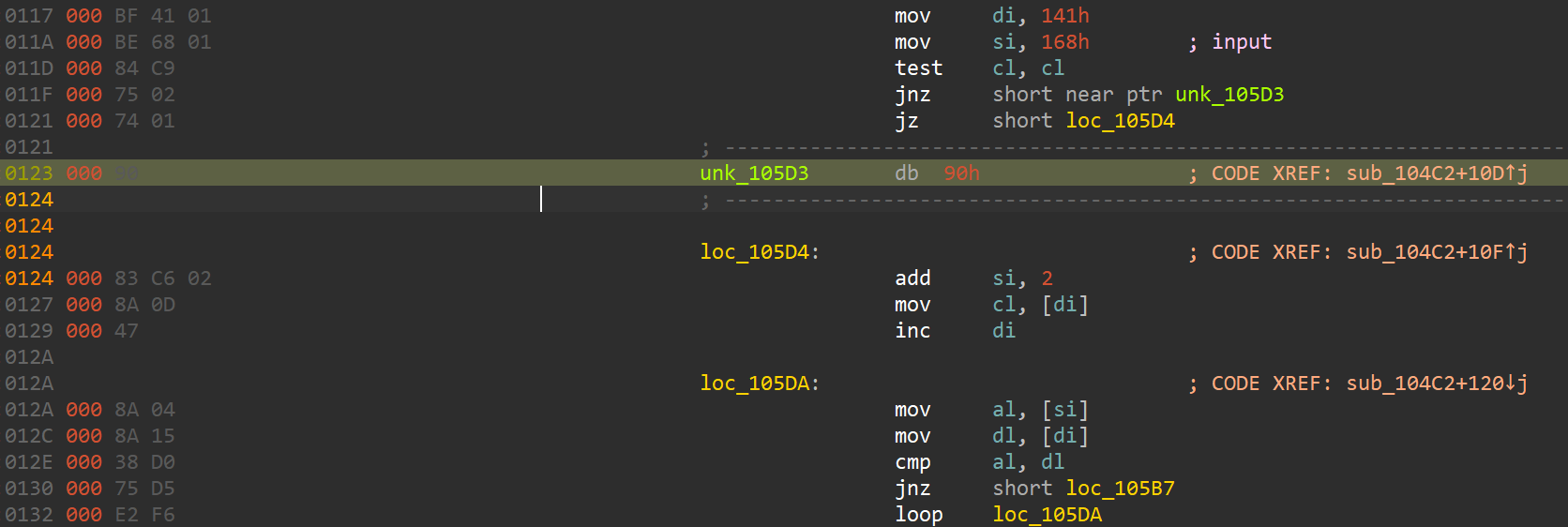
MS-DOS on Intel 8086. old but classic architecture
Directly examine the assembly code, a heavily modified RC4 and junk code are inspected. Don’t care about its internal implementation, the final XOR step remains unmodified. Hence extract the XOR Key in the proccess.
Junk code:
Debug:
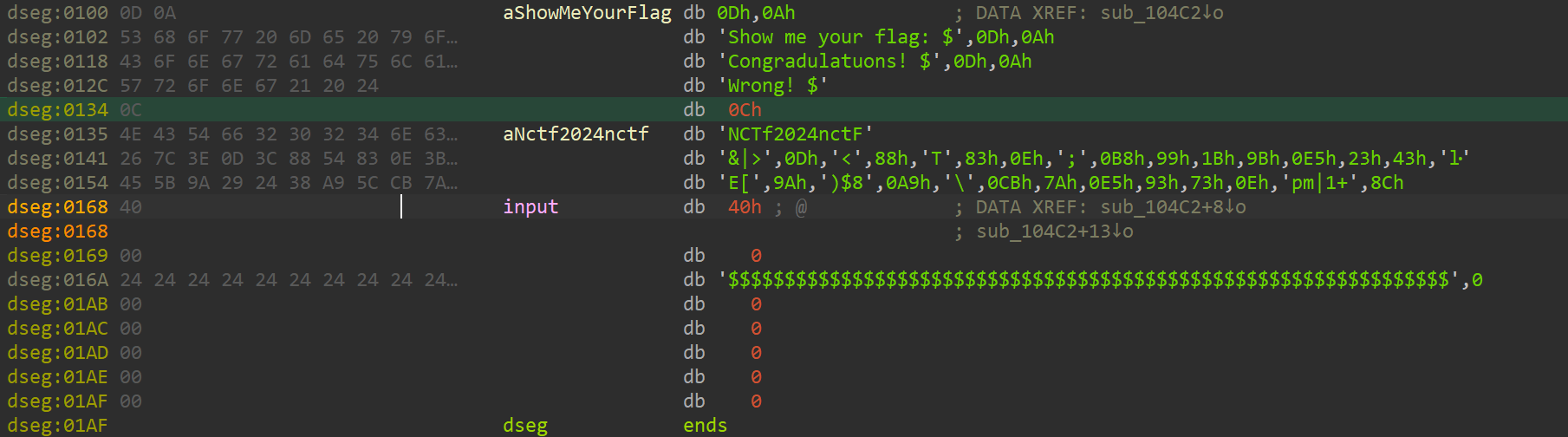
Input buffer structure in 8086 dos:
0x40(maxLength)+actualLength+data
1
2
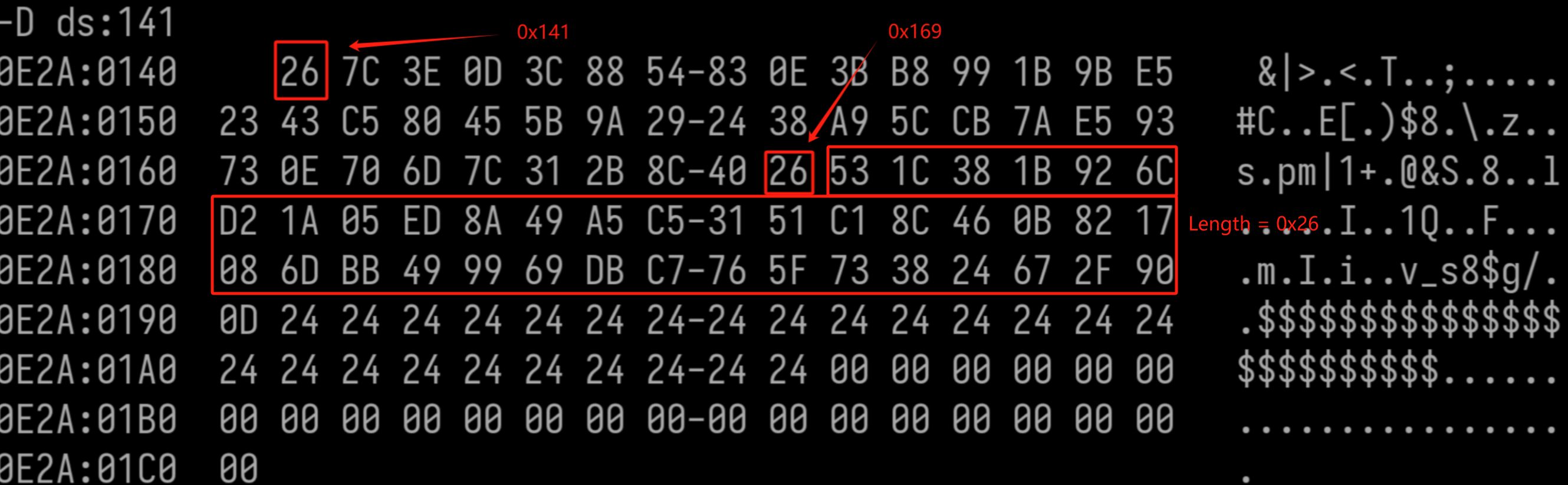
# 0x26 'a' chars: aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa,XORed
53 1C 38 1B 92 6C D2 1A 05 ED 8A 49 A5 C5 31 51 C1 8C 46 0B 82 17 08 6D BB 49 99 69 DB C7 76 5F 73 38 24 67 2F 90
1
2
# Key
32 7d 59 7a f3 0d b3 7b 64 8c eb 28 c4 a4 50 30 a0 ed 27 6a e3 76 69 0c da 28 f8 08 ba a6 17 3e 12 59 45 06 4e f1
1
2
# Cipher
7C 3E 0D 3C 88 54 83 0E 3B B8 99 1B 9B E5 23 43 C5 80 45 5B 9A 29 24 38 A9 5C CB 7A E5 93 73 0E 70 6D 7C 31 2B 8C
SafeProgram
The program monitors everything you do. So it reminds you: “DONOT DEBUG ME!”. But really?
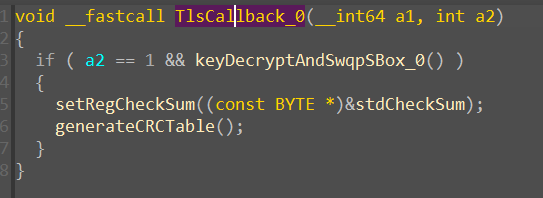
The main function implements SM4 encryption without modifying S-Box. Note that one dummy thread is continuously spawned / terminated, which triggers TLS each time.
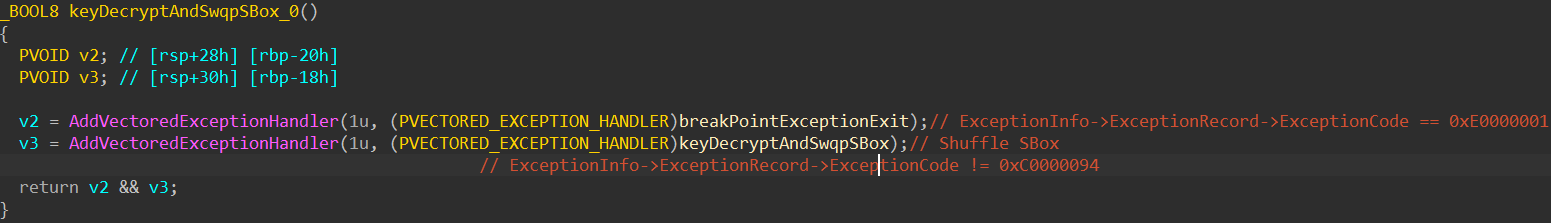
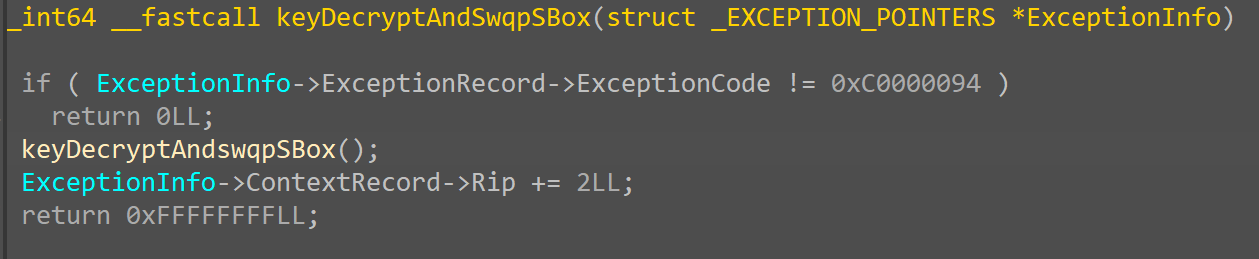
TLS then triggers CRC self-validation whenever a thread is created. By using a hardware breakpoint to bypass this validation, we can obtaining the hacked S-Box.
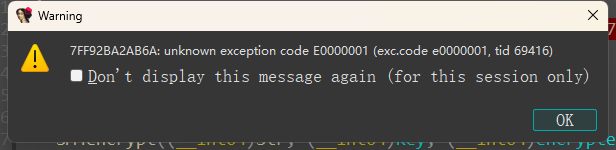
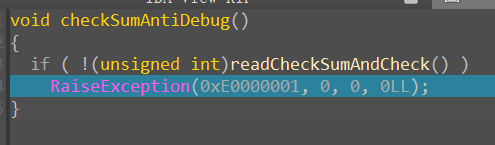
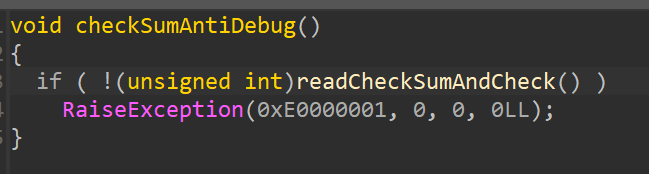
If we set software breakpoint, then 0xE0000001 exception occurred:
No(discard), F8 step over:
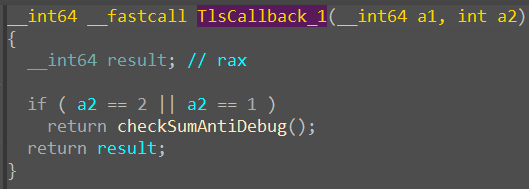
Now the callback functions were found:
- DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH (1): Process initialization
- DLL_THREAD_ATTACH (2): Thread creation
- DLL_THREAD_DETACH (3): Thread exit
- DLL_PROCESS_DETACH (0): Process termination
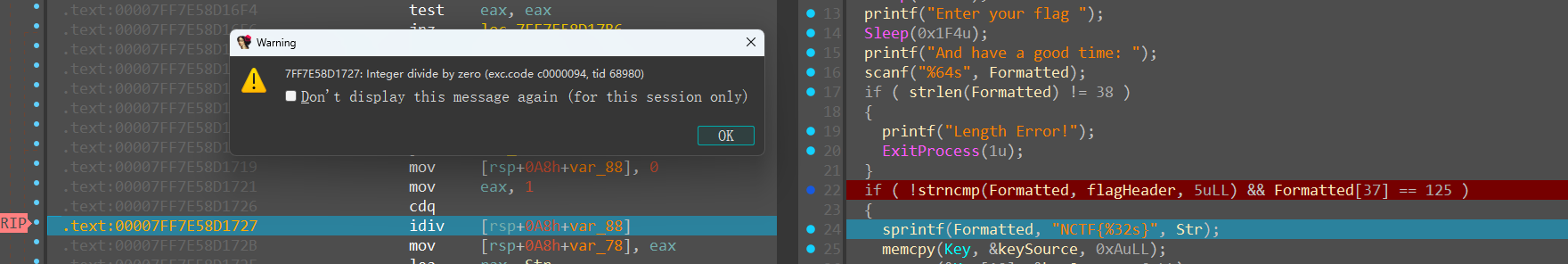
Divide by 0 exception:
The decrypted keySource array orchestrates a sequential substitution on SBox.
Extract necessary data, and write a decrypt script:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
import struct
# 系统参数
FK = [0xA3B1BAC6, 0x56AA3350, 0x677D9197, 0xB27022DC]
# 固定参数CK
CK = [
0x00070e15, 0x1c232a31, 0x383f464d, 0x545b6269,
0x70777e85, 0x8c939aa1, 0xa8afb6bd, 0xc4cbd2d9,
0xe0e7eef5, 0xfc030a11, 0x181f262d, 0x343b4249,
0x50575e65, 0x6c737a81, 0x888f969d, 0xa4abb2b9,
0xc0c7ced5, 0xdce3eaf1, 0xf8ff060d, 0x141b2229,
0x30373e45, 0x4c535a61, 0x686f767d, 0x848b9299,
0xa0a7aeb5, 0xbcc3cad1, 0xd8dfe6ed, 0xf4fb0209,
0x10171e25, 0x2c333a41, 0x484f565d, 0x646b7279
]
# 自定义S盒
SBox = [
0xD1, 0x90, 0xE9, 0xFE, 0xCC, 0xE1, 0x3D, 0xB7, 0x16, 0xB6,
0x14, 0xC2, 0x28, 0xFB, 0x2C, 0x05, 0x2B, 0x67, 0x9A, 0x76,
0x2A, 0xBE, 0x04, 0xC3, 0xAA, 0x44, 0x13, 0x26, 0x49, 0x86,
0x06, 0x99, 0x9C, 0x42, 0x50, 0xF4, 0x91, 0xEF, 0x98, 0x7A,
0x33, 0x54, 0x0B, 0x43, 0xED, 0xCF, 0xAC, 0x62, 0xE4, 0xB3,
0x17, 0xA9, 0x1C, 0x08, 0xE8, 0x95, 0x80, 0xDF, 0x94, 0xFA,
0x75, 0x8F, 0x3F, 0xA6, 0x47, 0x07, 0xA7, 0x4F, 0xF3, 0x73,
0x71, 0xBA, 0x83, 0x59, 0x3C, 0x19, 0xE6, 0x85, 0xD6, 0xA8,
0x68, 0x6B, 0x81, 0xB2, 0xFC, 0x64, 0xDA, 0x8B, 0xF8, 0xEB,
0x0F, 0x4B, 0x70, 0x56, 0x9D, 0x35, 0x1E, 0x24, 0x0E, 0x78,
0x63, 0x58, 0x9F, 0xA2, 0x25, 0x22, 0x7C, 0x3B, 0x01, 0x21,
0xC9, 0x87, 0xD4, 0x00, 0x46, 0x57, 0x5E, 0xD3, 0x27, 0x52,
0x4C, 0x36, 0x02, 0xE7, 0xA0, 0xC4, 0xC8, 0x9E, 0xEA, 0xBF,
0x8A, 0xD2, 0x40, 0xC7, 0x38, 0xB5, 0xA3, 0xF7, 0xF2, 0xCE,
0xF9, 0x61, 0x15, 0xA1, 0xE0, 0xAE, 0x5D, 0xA4, 0x9B, 0x34,
0x1A, 0x55, 0xAD, 0x93, 0x32, 0x30, 0xF5, 0x8C, 0xB1, 0xE3,
0x1D, 0xF6, 0xE2, 0x2E, 0x82, 0x66, 0xCA, 0x60, 0xC0, 0x29,
0x23, 0xAB, 0x0D, 0x53, 0x4E, 0x6F, 0xD5, 0xDB, 0x37, 0x45,
0xDE, 0xFD, 0x8E, 0x2F, 0x03, 0xFF, 0x6A, 0x72, 0x6D, 0x6C,
0x5B, 0x51, 0x8D, 0x1B, 0xAF, 0x92, 0xBB, 0xDD, 0xBC, 0x7F,
0x11, 0xD9, 0x5C, 0x41, 0x1F, 0x10, 0x5A, 0xD8, 0x0A, 0xC1,
0x31, 0x88, 0xA5, 0xCD, 0x7B, 0xBD, 0x2D, 0x74, 0xD0, 0x12,
0xB8, 0xE5, 0xB4, 0xB0, 0x89, 0x69, 0x97, 0x4A, 0x0C, 0x96,
0x77, 0x7E, 0x65, 0xB9, 0xF1, 0x09, 0xC5, 0x6E, 0xC6, 0x84,
0x18, 0xF0, 0x7D, 0xEC, 0x3A, 0xDC, 0x4D, 0x20, 0x79, 0xEE,
0x5F, 0x3E, 0xD7, 0xCB, 0x39, 0x48
]
def left_rotate(n, b):
return ((n << b) | (n >> (32 - b))) & 0xFFFFFFFF
def tau(b):
a = b.to_bytes(4, 'big')
a = [SBox[x] for x in a]
return int.from_bytes(bytes(a), 'big')
def L(b):
return b ^ left_rotate(b, 2) ^ left_rotate(b, 10) ^ left_rotate(b, 18) ^ left_rotate(b, 24)
def T(b):
return L(tau(b))
def L_prime(b):
return b ^ left_rotate(b, 13) ^ left_rotate(b, 23)
def T_prime(b):
return L_prime(tau(b))
def sm4_key_expansion(key):
MK = struct.unpack('>4I', key)
K = [0] * 36
K[0] = MK[0] ^ FK[0]
K[1] = MK[1] ^ FK[1]
K[2] = MK[2] ^ FK[2]
K[3] = MK[3] ^ FK[3]
rk = [0] * 32
for i in range(32):
tmp = K[i+1] ^ K[i+2] ^ K[i+3] ^ CK[i]
tmp = T_prime(tmp)
K[i+4] = K[i] ^ tmp
rk[i] = K[i+4]
return rk
def sm4_decrypt(ciphertext, rk):
x = list(struct.unpack('>4I', ciphertext))
for i in range(32):
rk_i = rk[i]
tmp = x[i+1] ^ x[i+2] ^ x[i+3] ^ rk_i
tmp = T(tmp)
x.append(x[i] ^ tmp)
return struct.pack('>4I', x[35], x[34], x[33], x[32])
# 输入数据
key = bytes([0x4E, 0x43, 0x54, 0x46, 0x32, 0x34, 0x6E, 0x63, 0x74, 0x66,
0x4E, 0x43, 0x54, 0x46, 0x32, 0x34])
cipher = bytes([0xFB, 0x97, 0x3C, 0x3B, 0xF1, 0x99, 0x12, 0xDF, 0x13, 0x30,
0xF7, 0xD8, 0x7F, 0xEB, 0xA0, 0x6C, 0x14, 0x5B, 0xA6, 0x2A,
0xA8, 0x05, 0xA5, 0xF3, 0x76, 0xBE, 0xC9, 0x01, 0xF9, 0x36,
0x7B, 0x46])
# 生成轮密钥并反转
rk = sm4_key_expansion(key)
dec_rk = rk[::-1]
# 分块解密
block1 = cipher[:16]
block2 = cipher[16:]
plain1 = sm4_decrypt(block1, dec_rk)
plain2 = sm4_decrypt(block2, dec_rk)
plain = plain1 + plain2
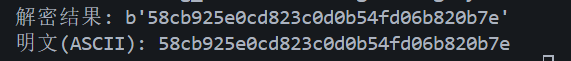
print("Decrypted:", plain)
Appendix
Standard SBox for SM4:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
00 | D6 90 E9 FE CC E1 3D B7 16 B6 14 C2 28 FB 2C 05
10 | 2B 67 9A 76 2A BE 04 C3 AA 44 13 26 49 86 06 99
20 | 9C 42 50 F4 91 EF 98 7A 33 54 0B 43 ED CF AC 62
30 | E4 B3 1C A9 C9 08 E8 95 80 DF 94 FA 75 8F 3F A6
40 | 47 07 A7 FC F3 73 17 BA 83 59 3C 19 E6 85 4F A8
50 | 68 6B 81 B2 71 64 DA 8B F8 EB 0F 4B 70 56 9D 35
60 | 1E 24 0E 5E 63 58 D1 A2 25 22 7C 3B 01 21 78 87
70 | D4 00 46 57 9F D3 27 52 4C 36 02 E7 A0 C4 C8 9E
80 | EA BF 8A D2 40 C7 38 B5 A3 F7 F2 CE F9 61 15 A1
90 | E0 AE 5D A4 9B 34 1A 55 AD 93 32 30 F5 8C B1 E3
A0 | 1D F6 E2 2E 82 66 CA 60 C0 29 23 AB 0D 53 4E 6F
B0 | D5 DB 37 45 DE FD 8E 2F 03 FF 6A 72 6D 6C 5B 51
C0 | 8D 1B AF 92 BB DD BC 7F 11 D9 5C 41 1F 10 5A D8
D0 | 0A C1 31 88 A5 CD 7B BD 2D 74 D0 12 B8 E5 B4 B0
E0 | 89 69 97 4A 0C 96 77 7E 65 B9 F1 09 C5 6E C6 84
F0 | 18 F0 7D EC 3A DC 4D 20 79 EE 5F 3E D7 CB 39 48
Structure I used
1
2
3
4
typedef struct _EXCEPTION_POINTERS {
PEXCEPTION_RECORD ExceptionRecord;
PCONTEXT ContextRecord;
} EXCEPTION_POINTERS, *PEXCEPTION_POINTERS;
1
2
3
4
5
void NTAPI TlsCallback(
PVOID DllHandle,
DWORD Reason,
PVOID Reserved
);